
Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase Regulation of Glycolysis Metabolism
Hexokinase is the initial enzyme of glycolysis, catalyzing the phosphorylation of glucose by ATP to glucose-6-P. It is one of the rate-limiting enzymes of glycolysis. Its activity declines rapidly as normal red cells age.
10 Difference between Hexokinase and Glucokinase
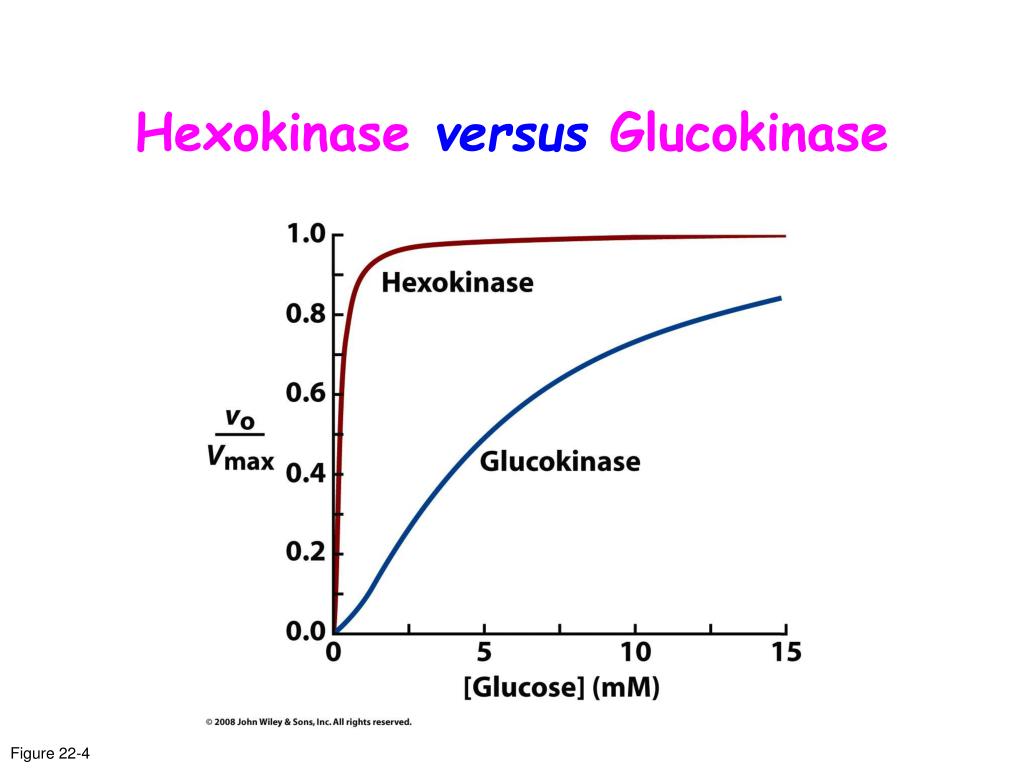
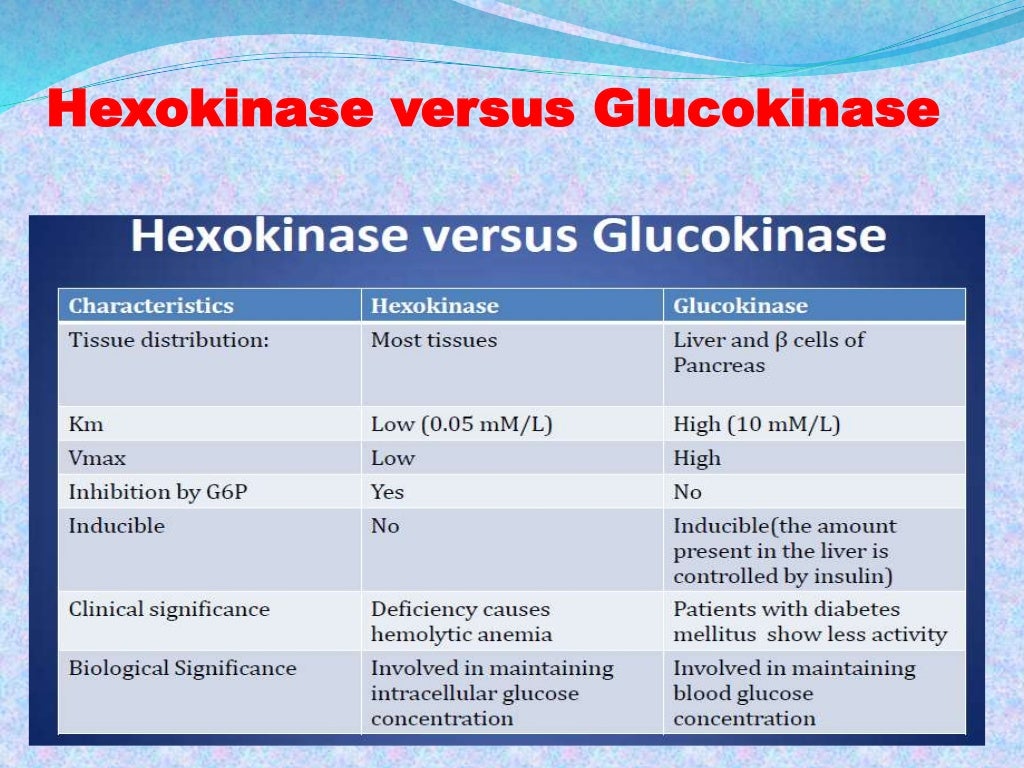
Glucokinase is also saturated at a much higher glucose concentration than hexokinase, so it's able to keep up with the large amount of glucose, whereas hexokinase would be overwhelmed. In other words, glucokinase has a higher VMAX (maximum reaction rate).
Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase Definition, Mechanism And Function
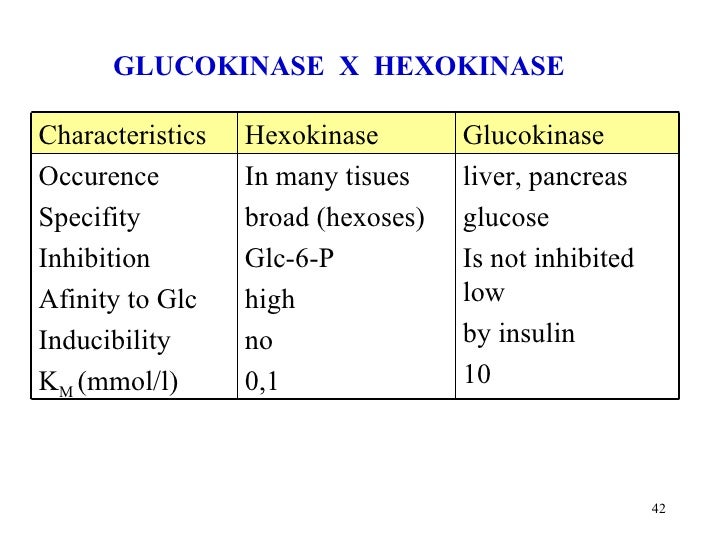
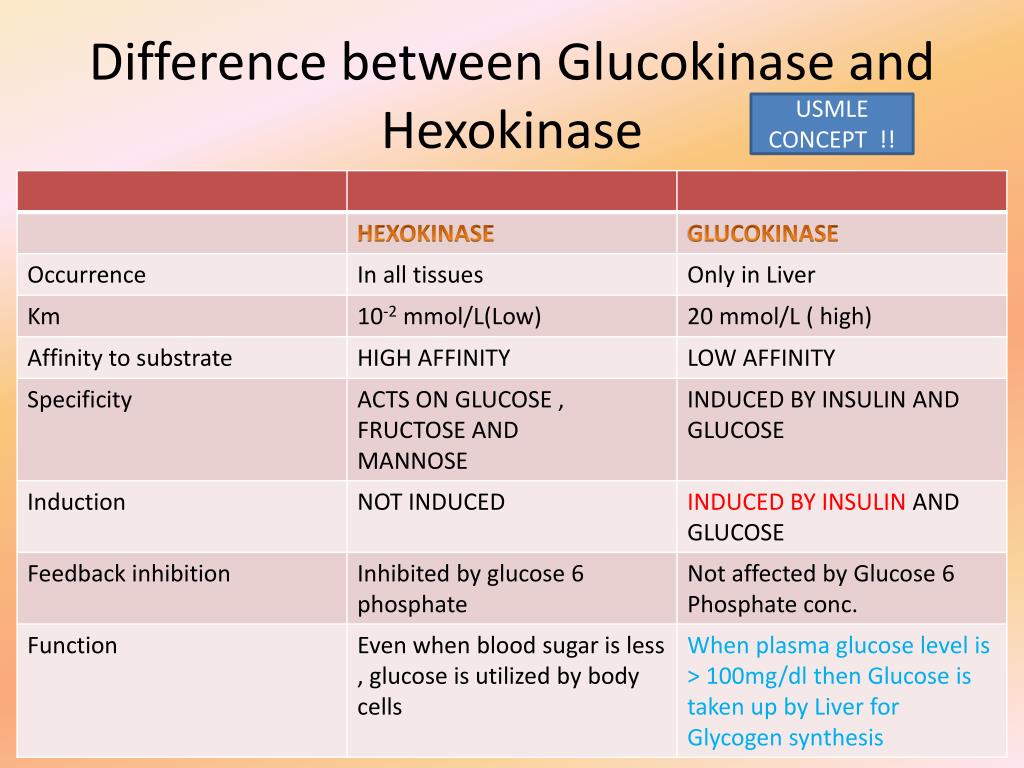
Here are some of the difference between both. 1: Site of Action:- Hexokinase is present in all tissues (Except) the liver and B-cells of pancreas whereas, Glucokinase is present in both Liver and B-cells of pancreas. 2: Activity:- The activity of glucokinase depends upon the nutritional stat of glucose.
Sach1bi1 11 angl
Glucokinase has a lower affinity for glucose than the other hexokinases do, and its activity is localized to a few cell types, leaving the other three hexokinases as more important preparers of glucose for glycolysis and glycogen synthesis for most tissues and organs.

Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase Importance and Clinical Significance YouTube
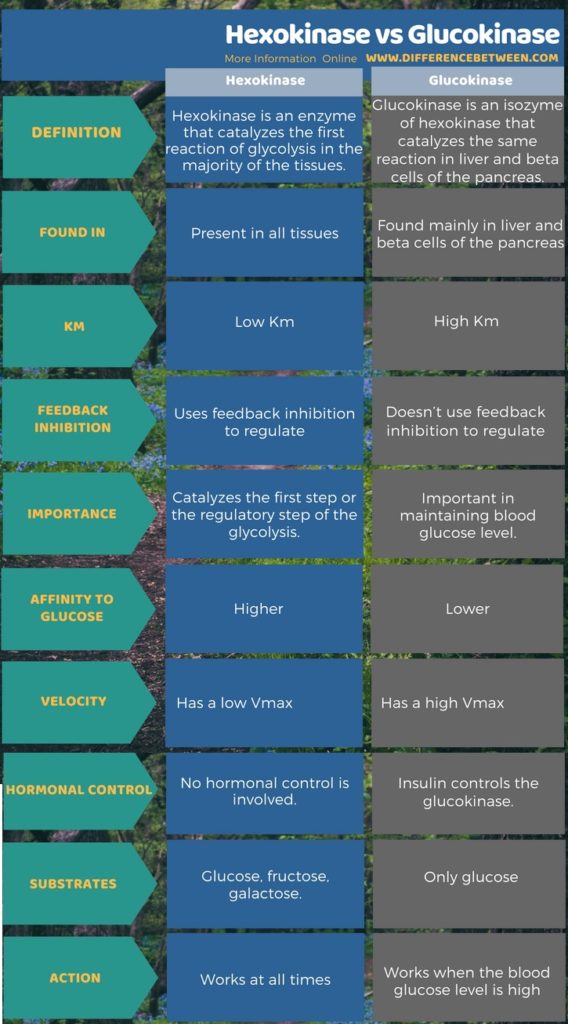
The main difference between hexokinase and glucokinase is that the hexokinase is an enzyme present in all cells whereas the glucokinase is an enzyme only present in the liver. Furthermore, hexokinase has a high affinity towards glucose while glucokinase has a low affinity towards glucose.

Figure 3 from Role of Glucokinase in the Subcellular Localization of
Hexokinase is a ubiquitous enzyme catalyzing glucose phosphorylation, while glucokinase, a specific hexokinase variant, functions primarily in the liver and pancreas with a higher glucose affinity. Key Differences Hexokinase is a general term for enzymes that phosphorylate six-carbon sugars, initiating glycolysis.
PPT Glycolysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6955258
Hexokinase is actually a broader term for a class of enzymes that phosphorylates six-carbon sugars (glucose, fructose, galactose etc.), while glucokinase is a specific type of hexokinase (an isoform) that has a lower affinity for substrates and exclusively works with glucose, rather than other 6-carbon sugars.
Hexokinase Vs Glucokinase Definition, Mechanism And Function
Glucokinase (GCK, hexokinase IV) is a monomeric enzyme that catalyzes the ATP-dependent conversion of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate, the first and rate-limiting step of glycolysis in the liver and pancreas. [ 1, 2] GCK was first discovered in the early 1960's, and shortly thereafter it became the subject of intense study due to its unique sigmo.
PPT Basic Concepts in Metabolism and Regulation of Blood sugar levels
Our data on hexokinase and glucokinase expression point out an absence of cross regulation mechanisms at the transcription level and different regulatory pathways. In the presence of glucose, CaHxk2 migrates in the nucleus and contributes to the glucose repression signaling pathway. In addition, CaHxk2 participates to oxidative, osmotic and.
Glycolysis tca
This video provides a tutorial on important difference between hexokinase and glucokinase enzyme. Hexokinase enzyme has low Km (0.1 mM, high affinity for substrate) and low Vmax) low-capacity.

Biochemistry Answer Hexokinase Click the link in our bio for an
Glucose is an aldose-monosaccharide having the chemical formula of CHO. Humans derive glucose by consuming food of plant or animal origin. Complex carbohydrates present in these foods are digested in the gastrointestinal tract, converted to simple monosaccharides, and absorbed. [1] [2] [1]

The Network of GlucokinaseExpressing Cells in Glucose Homeostasis and
Glucokinase / metabolism Hexokinase / genetics* Hexokinase / metabolism Humans Isoenzymes / genetics* Isoenzymes / metabolism Molecular Structure Sequence Homology, Nucleic Acid.

Glucokinase vs Hexokinase Glycogenesis Glycolytic Enzymes Dr
Glucokinase (GK) belongs to the hexokinase family (Grossbard and Schimke, 1966). It catalyzes the phosphorylation of a glucose molecule to produce glucose 6-phosphate and plays an important role in glucose utilization and metabolism in the liver and pancreas (Al-Hasani et al., 2003).
What is the differences between hexokinase and glucokinase? Medical
Home enzymes 10 Difference between Hexokinase and Glucokinase Both Hexokinase and Glucokinase are enzymes catalyzing the phophorylation of Glucose to Glucose-6-phosphate using ATP. During the reaction, one ATP molecule is cleaved to ADP and the phosphate thus released is added to glucose.
Difference Between Hexokinase and Glucokinase Compare the Difference
Hexokinase (HXK) is a critical enzyme in the glycolytic pathway and displays a wide range of functions in different organisms such as fungi, parasites, mammals, and plants. This review discusses HXKs moonlighting functions in depth since they have a profound impact on the responses to nutritional, environmental, and disease challenges.

Glucokinase Vs Hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that irreversibly phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars ), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexokinase possesses the ability to transfer an inorganic phosphate group from ATP to a substrate.