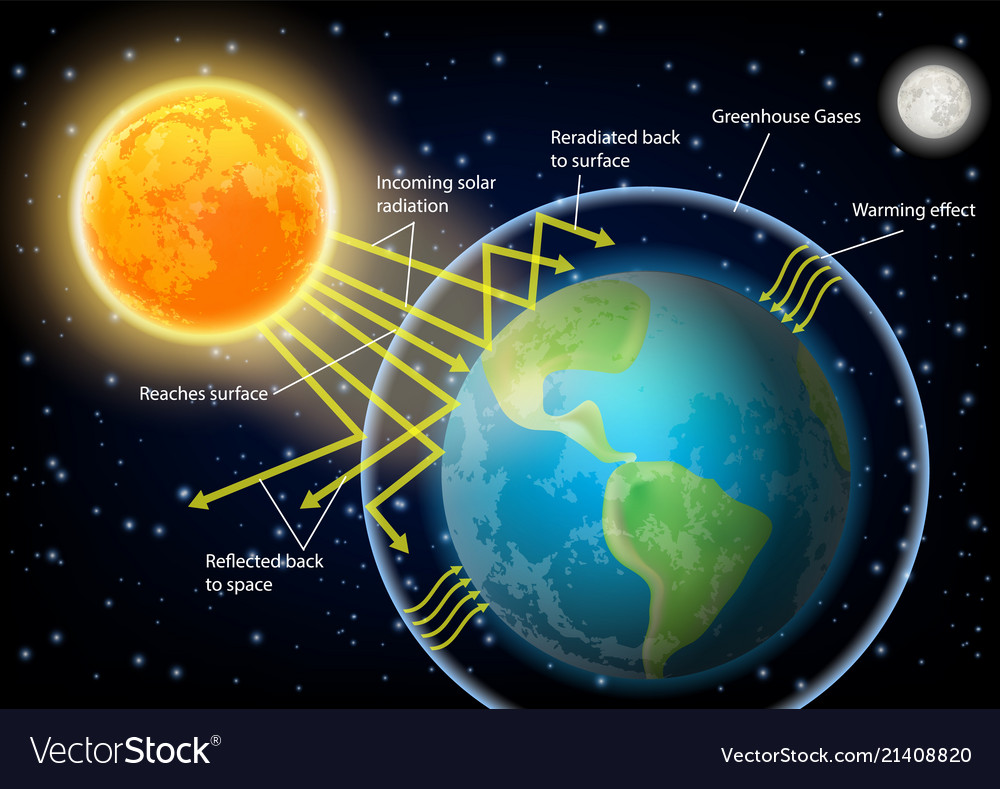
Greenhouse effect diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
Greenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and water vapor significantly affect the amount of energy in the Earth system, even though they make up a tiny percentage of Earth's atmosphere. Solar radiation that passes through the atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface is either reflected or absorbed.

Earth's Greenhouse Effect NYS Dept. of Environmental Conservation
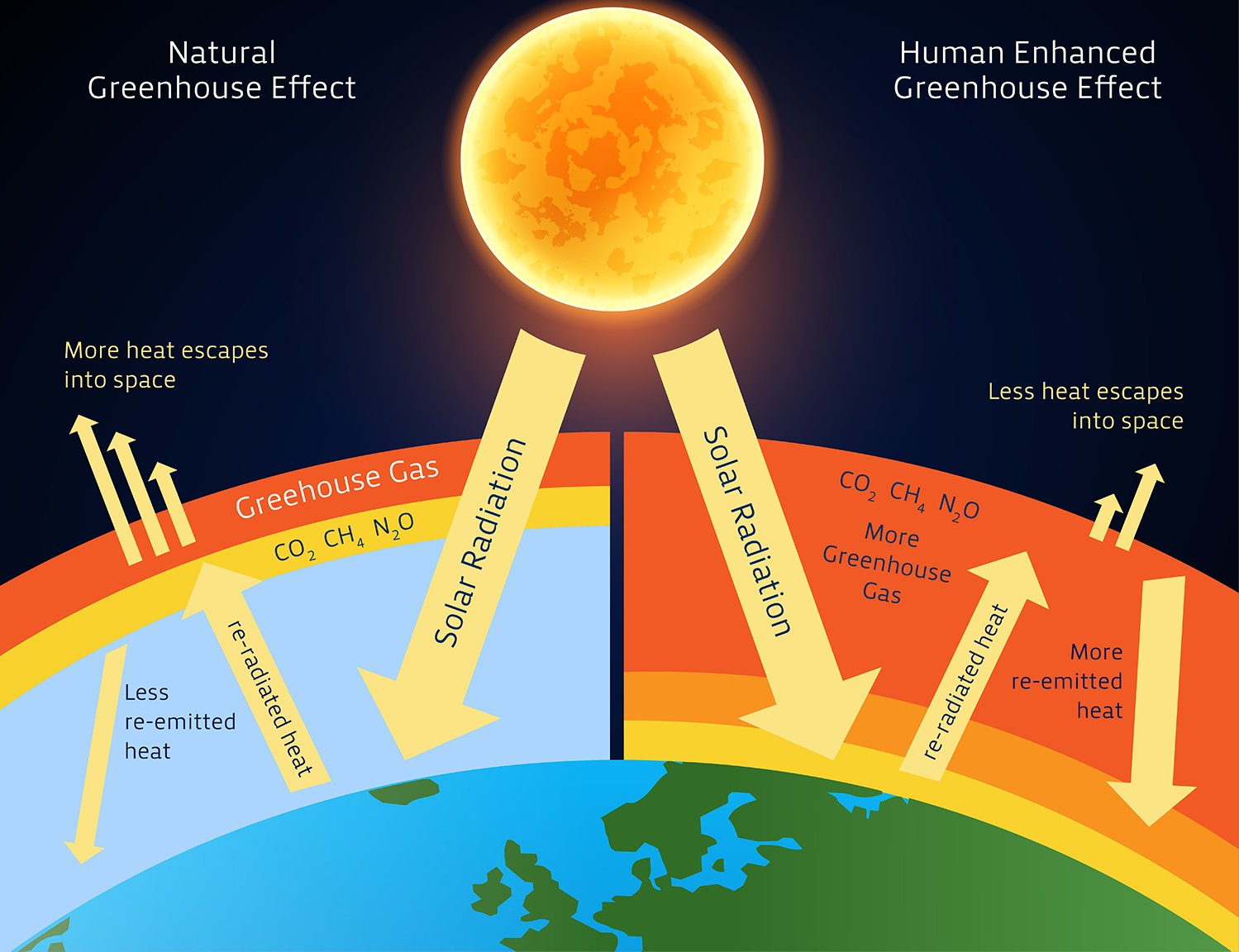
The scientific consensus is clear: through alterations of the carbon cycle, humans are changing the global climate by increasing the effects of something known as the greenhouse effect. Figure 21.1.a 21.1. a : This graph shows the predicted temperatures from two climate models and observed temperatures from 1880 to 2020.
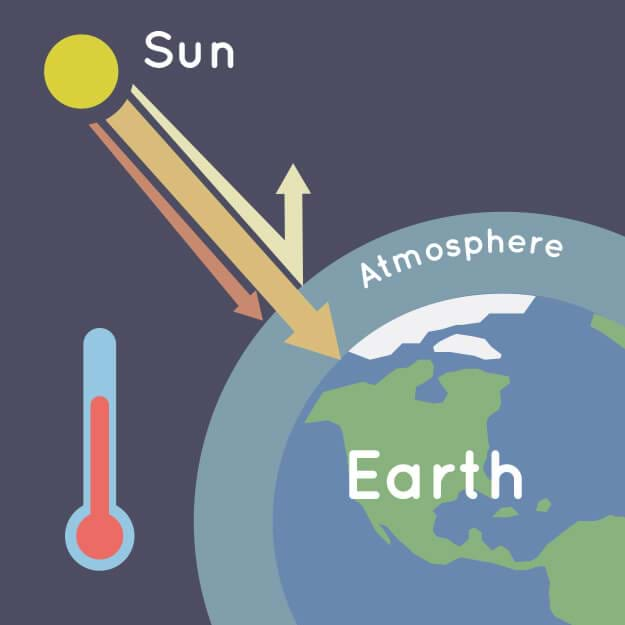
Amplified Greenhouse Effect Unit TeachEngineering
How Does the Greenhouse Effect Work? Solar energy absorbed at Earth's surface is radiated back into the atmosphere as heat. As the heat makes its way through the atmosphere and back out to space, greenhouse gases absorb much of it. Why do greenhouse gases absorb heat?
The Electronic Art of Environmental Activism (Part 1) In the Sportlight
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases.. Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from.
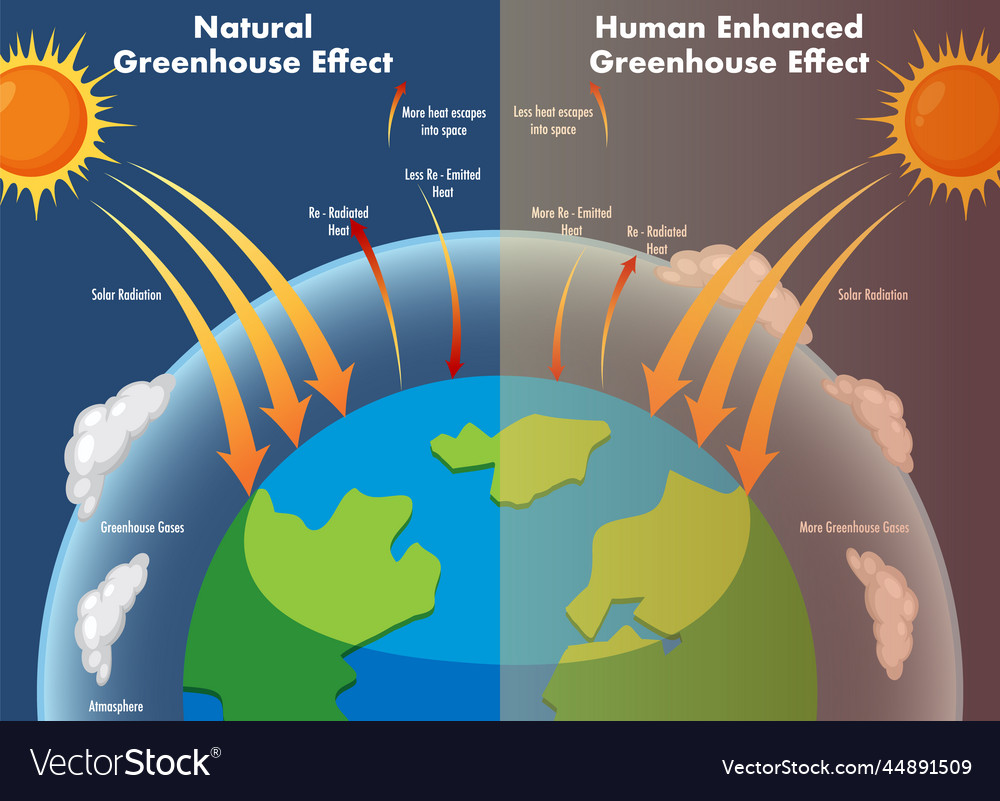
Diagram showing the greenhouse effect Royalty Free Vector
The Diagram shows Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide are the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouse gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation, etc. The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount of these gases in the atmosphere.

The ImpEE Project Improving Engineering Education
The greenhouse effect on Earth is defined as: "The infrared radiative effect of all infrared absorbing constituents in the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases (GHGs), clouds, and some aerosols absorb terrestrial radiation emitted by the Earth's surface and elsewhere in the atmosphere." [15] : 2232
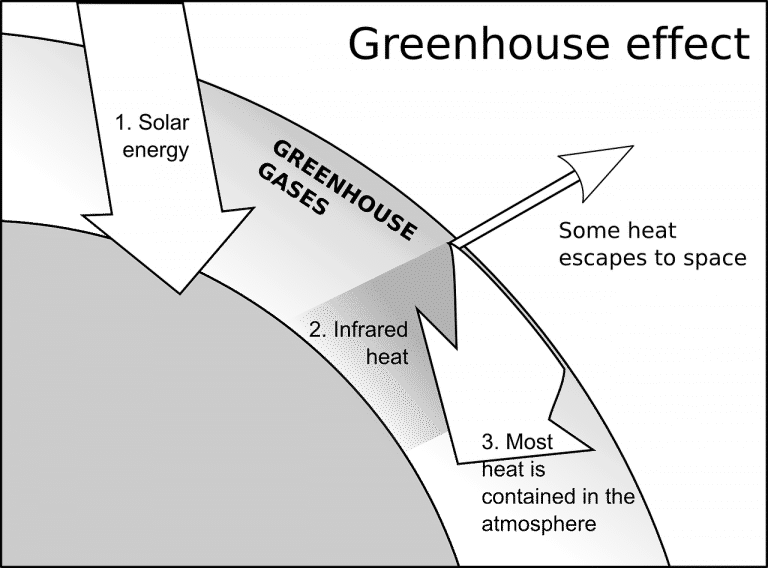
What is Greenhouse effect, its causes & Natural Energy Hub
The Carbon Cycle Diagram (suitable for an overhead projector transparency) (pdf) The Greenhouse Effect Diagram (suitable for an overhead projector transparency) (pdf) Sources of CO2 Emissions (pdf) Introduction/Motivation (Ask students to do a "splash sheet" about the greenhouse effect and global warming.
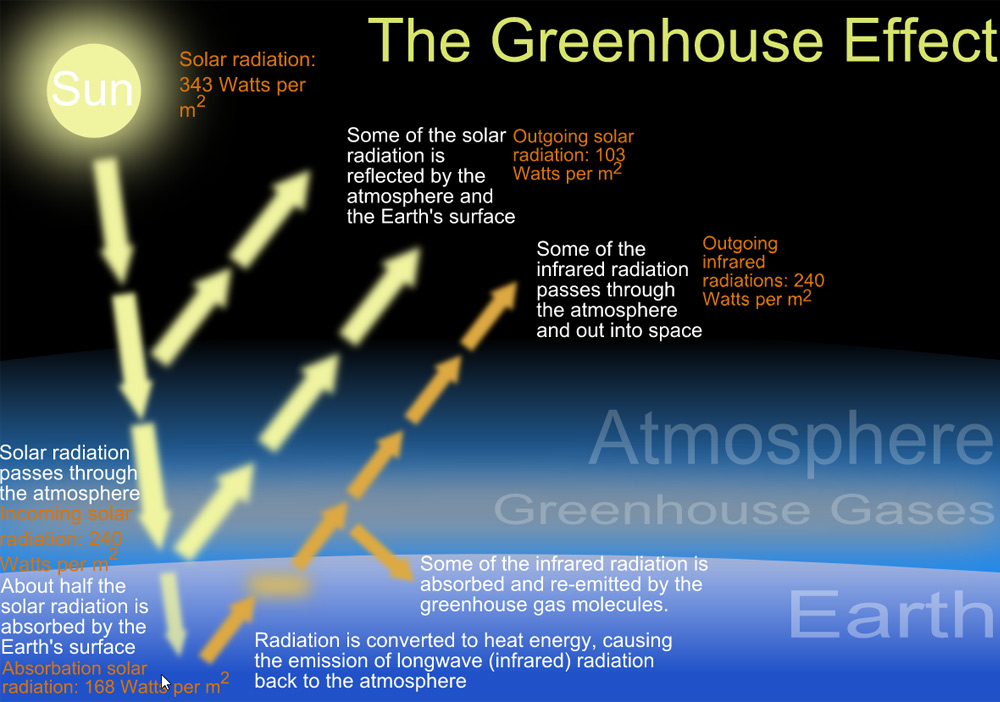
How does a Greenhouse Work? Explanation & Diagram
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat. This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes Earth a comfortable place to live. What Is the Greenhouse Effect?

Climate Change Environmental Center University of Colorado Boulder
Photograph Article Vocabulary Global warming describes the current rise in the average temperature of Earth's air and oceans. Global warming is often described as the most recent example of climate change. Earth's climate has changed many times.

Greenhouse Effect
greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclear.
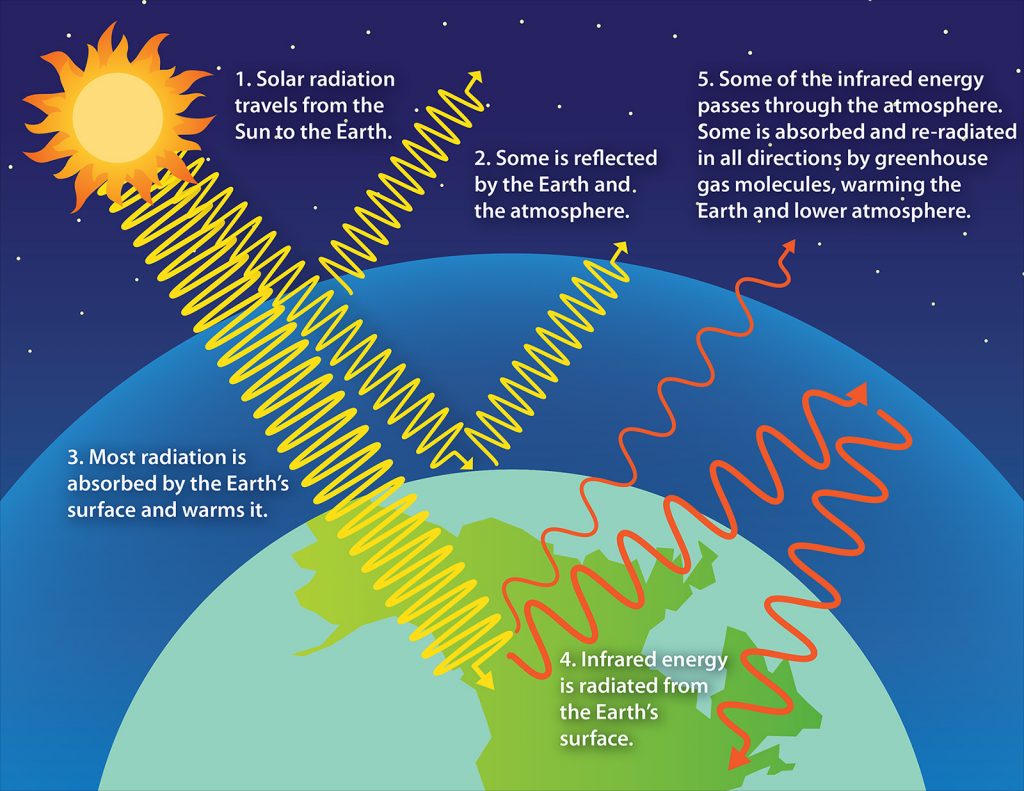
Greenhouse effect Understanding Global Change
A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech (Download en español.) Related. Color-coded map of changing global surface temperature anomalies from 1880 through 2022. Video: Global Warming from 1880 to 2022

ESRL Global Monitoring Laboratory Education and Outreach
The greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life. Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent it from escaping into space. About half of the sun's radiation that.
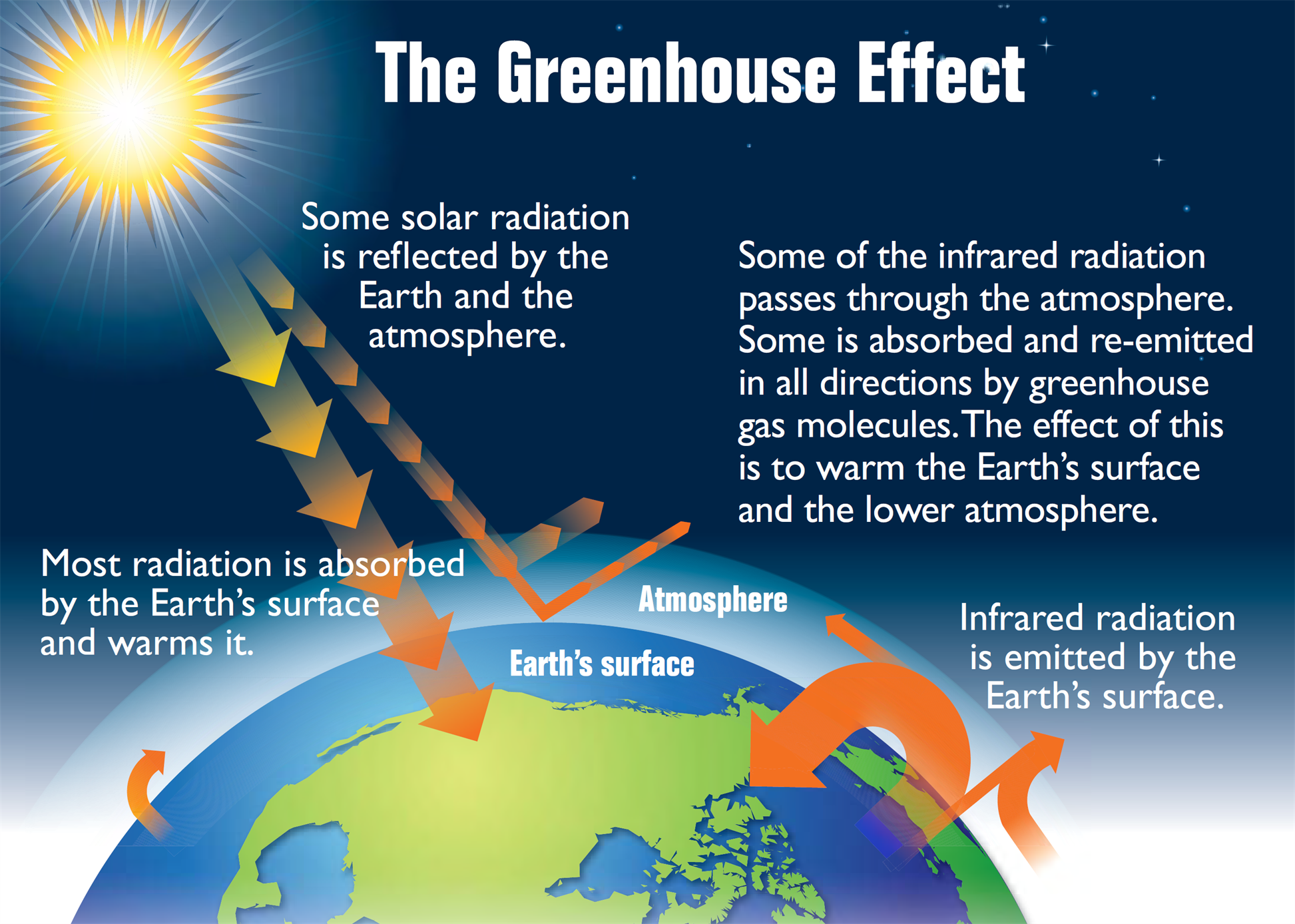
Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect Causes, Effects, and its Preventions
The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect . How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's.

greenhouse effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
Graphic: The Greenhouse Effect May 22, 2019 A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect. Also find this animated gif on our Causes page. Credit NASA-JPL/Caltech Downloads 768x432 7.44 MB image/gif Download 1920x1080 5.33 MB video/mp4 Download en español 1920x1080 5.54 MB video/mp4 Download en español 768px 7.22 MB image/gif Download

Diagram showing the greenhouse effect Royalty Free Vector
Planet Earth What Is the Greenhouse Effect? References By Marc Lallanila published 8 March 2018 (Image credit: Shutterstock) While other planets in Earth's solar system are either scorching hot.

Self Regulating Systems
The Greenhouse Effect A greenhouse is for growing plants. It is made of glass or clear plastic to let in lots of sunlight. But why not just put the plants outside? A greenhouse stays warmer than the air outside. Instead of cooling off at night, it traps some of the heat inside to keep the plants warm.