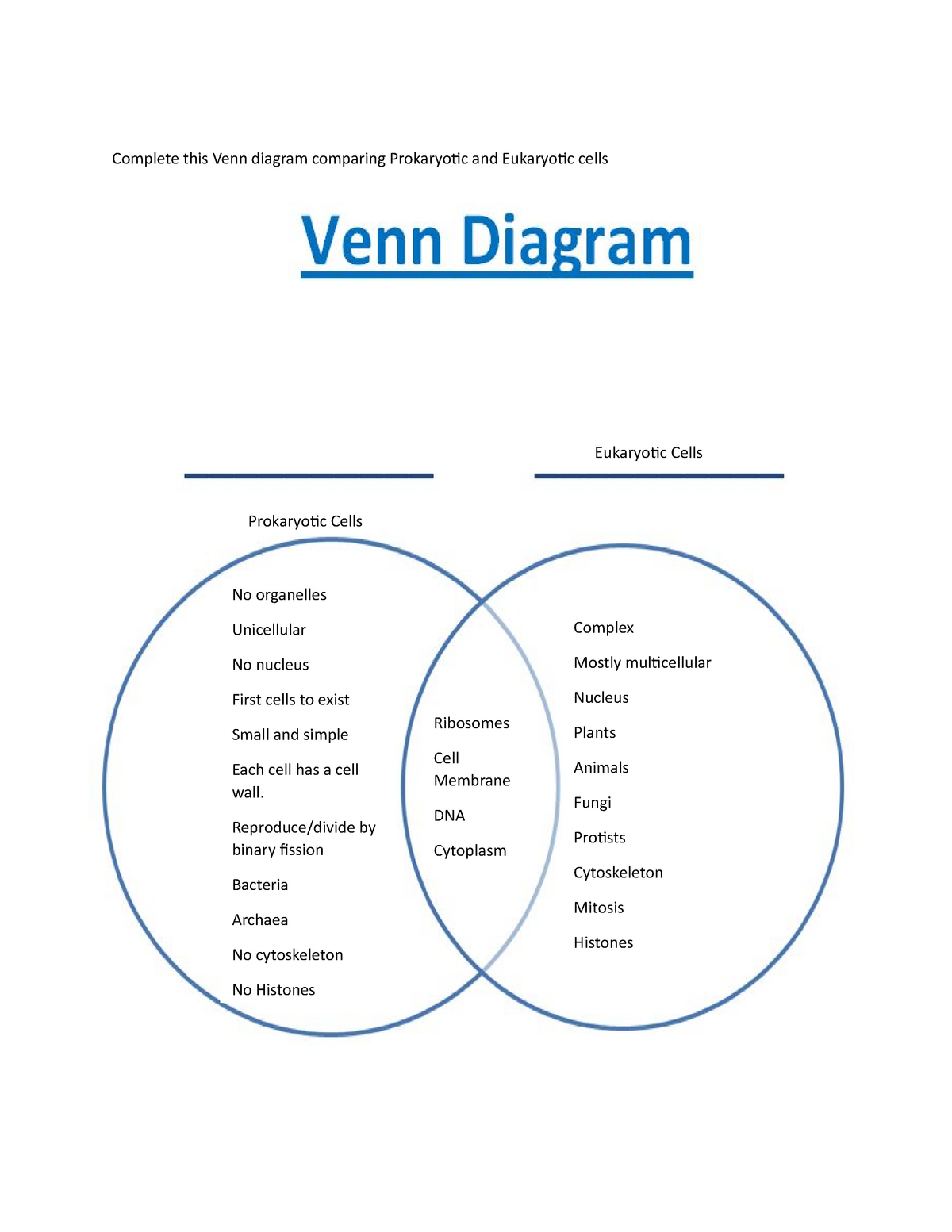
Venn diagram student handout Complete this Venn diagram comparing
Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotic cells are cells without a nucleus. The DNA in prokaryotic cells is in the cytoplasm rather than enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, like the one shown in Figure below.Organisms with prokaryotic cells are called prokaryotes.They were the first type of organisms to evolve and are still the.
Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote Venn Diagram Wiring Diagram Database
Prokaryotic cells also have a cell wall and may have flagella for movement. A Venn diagram is a useful tool to compare and contrast different elements. When comparing eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, a Venn diagram can help visualize the similarities and differences between the two cell types.

Wiring Diagram Database Venn Diagram Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic
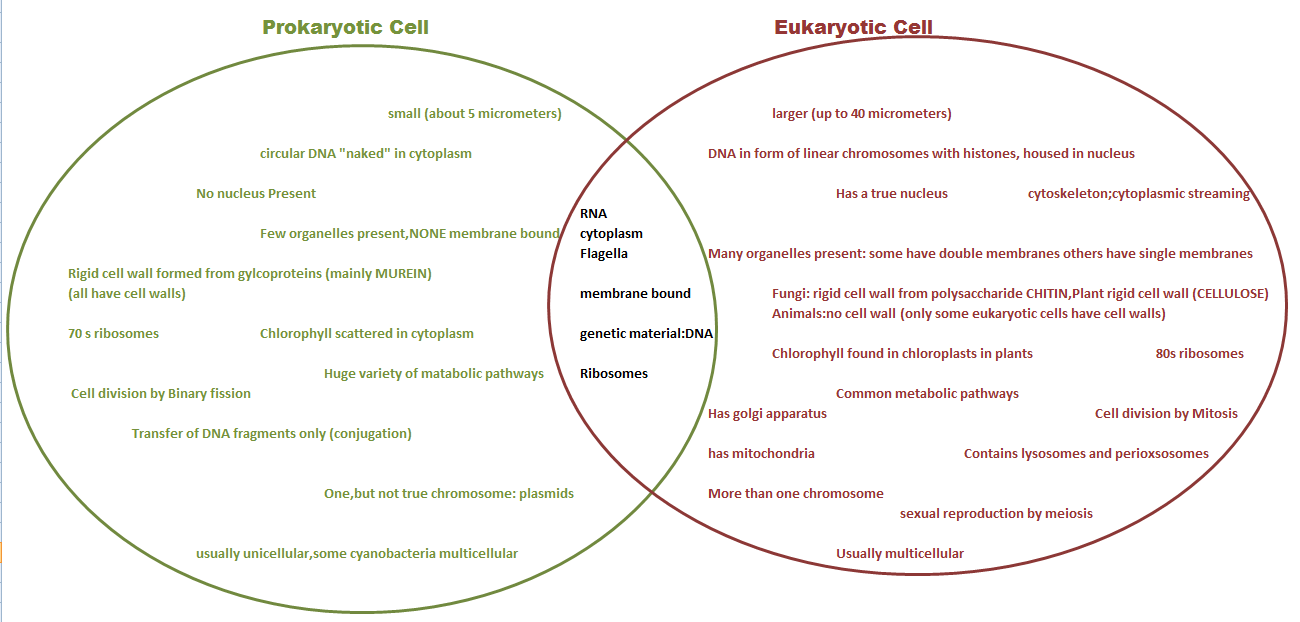
Since the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Venn diagram is a basic two circle Venn diagram, it can provide enough information. However, it is necessary to be careful with the kind of information you're inserting. The given diagram talks about the characteristics of prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
10 Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Current School News
At 0.1-5.0 μm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10-100 μm ( Figure 5.2.3 5.2. 3 ). The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell.

Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Venn Diagram Biology Pinterest
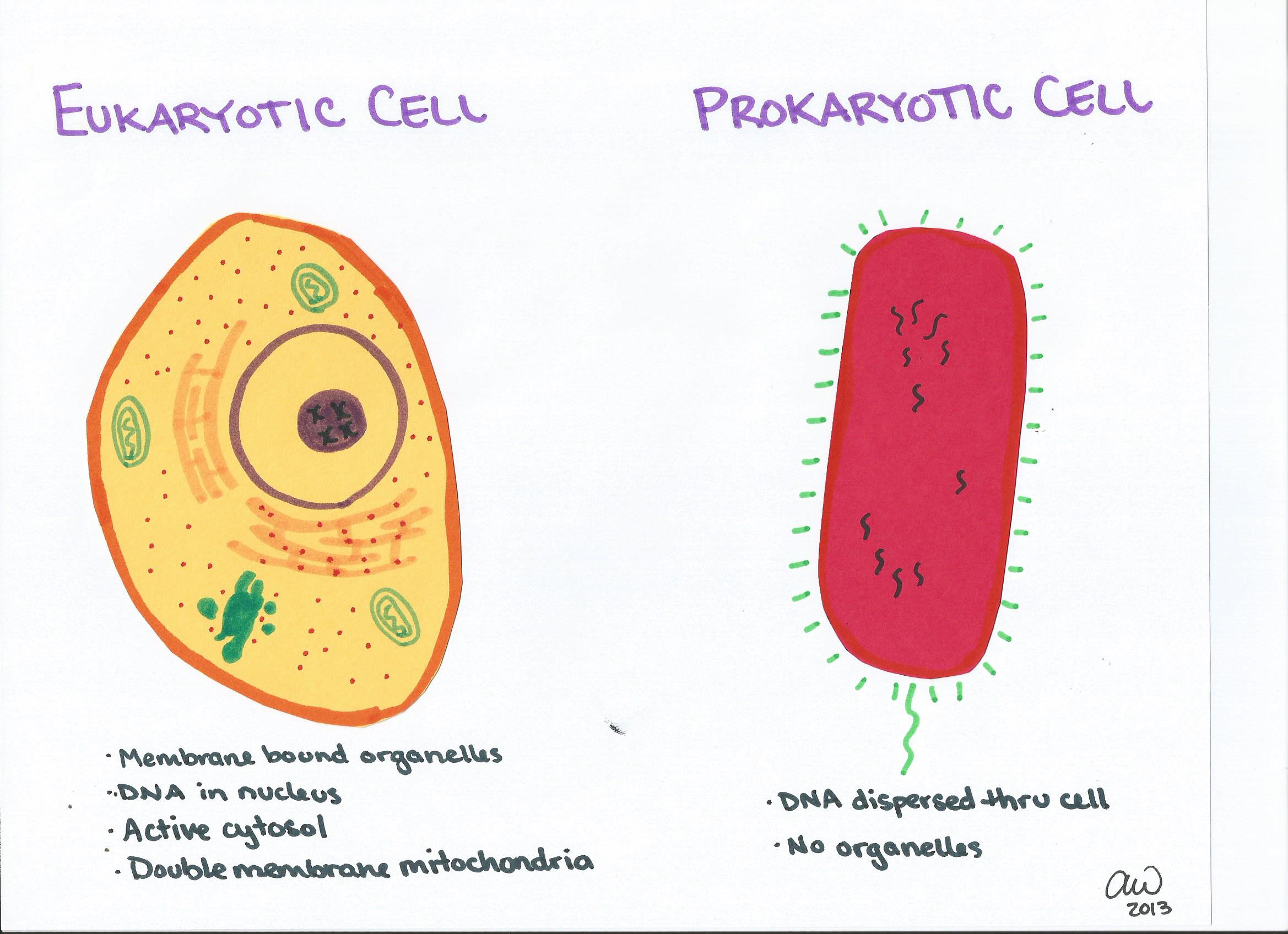
AboutTranscript. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles (such as the nucleus and mitochondria), while prokaryotic cells do not. DNA in eukaryotic cells is found inside the nucleus, while DNA in prokaryotic cells is located in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
Differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. biochemanics
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Venn Diagram is an illustrative tool that visually showcases the similarities and differences between these two types of cellular organisms.. Key features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting their distinct characteristics and functions.. Customize the editable template to meet your specific educational needs.Simplify the understanding of prokaryotic and.
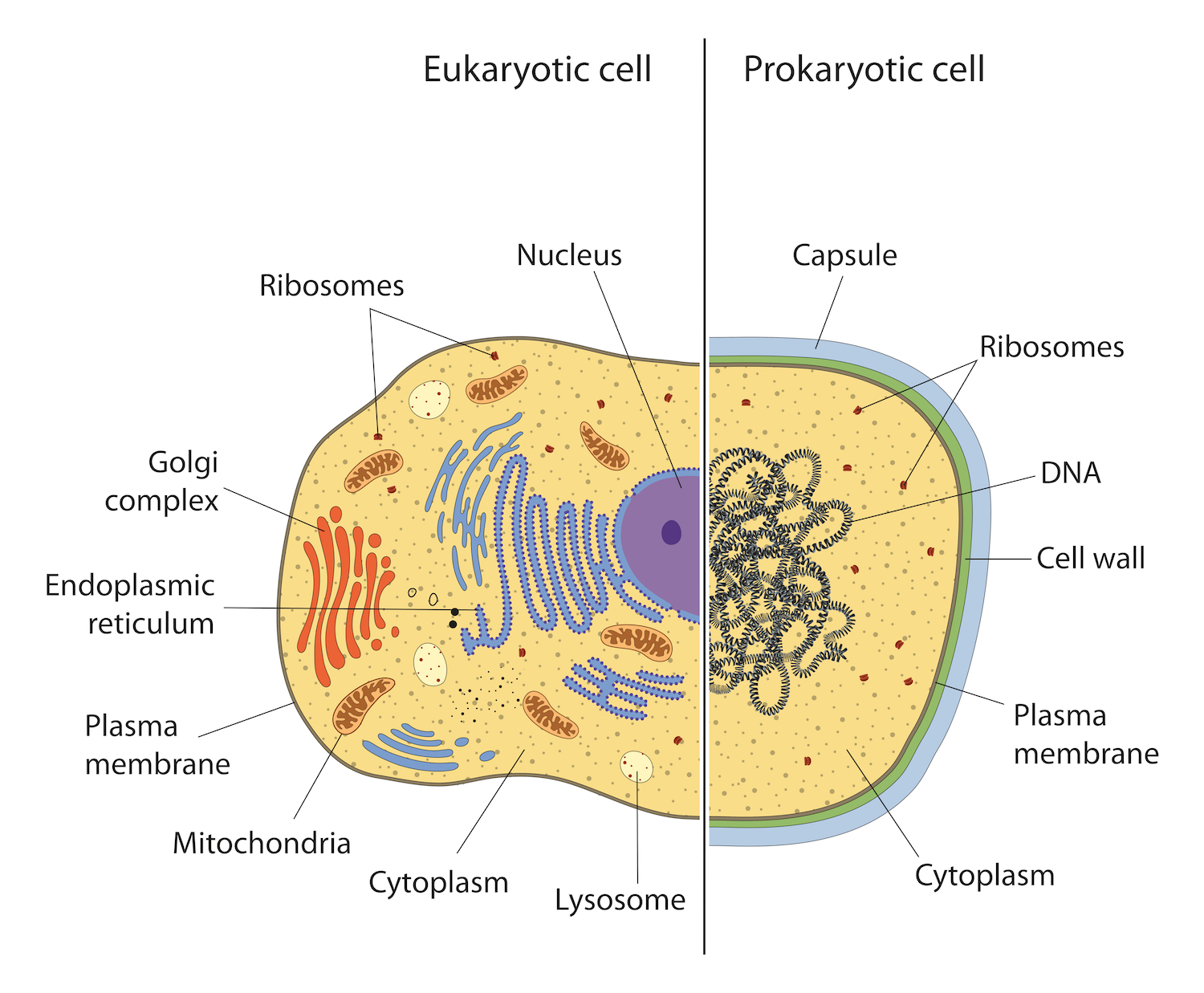
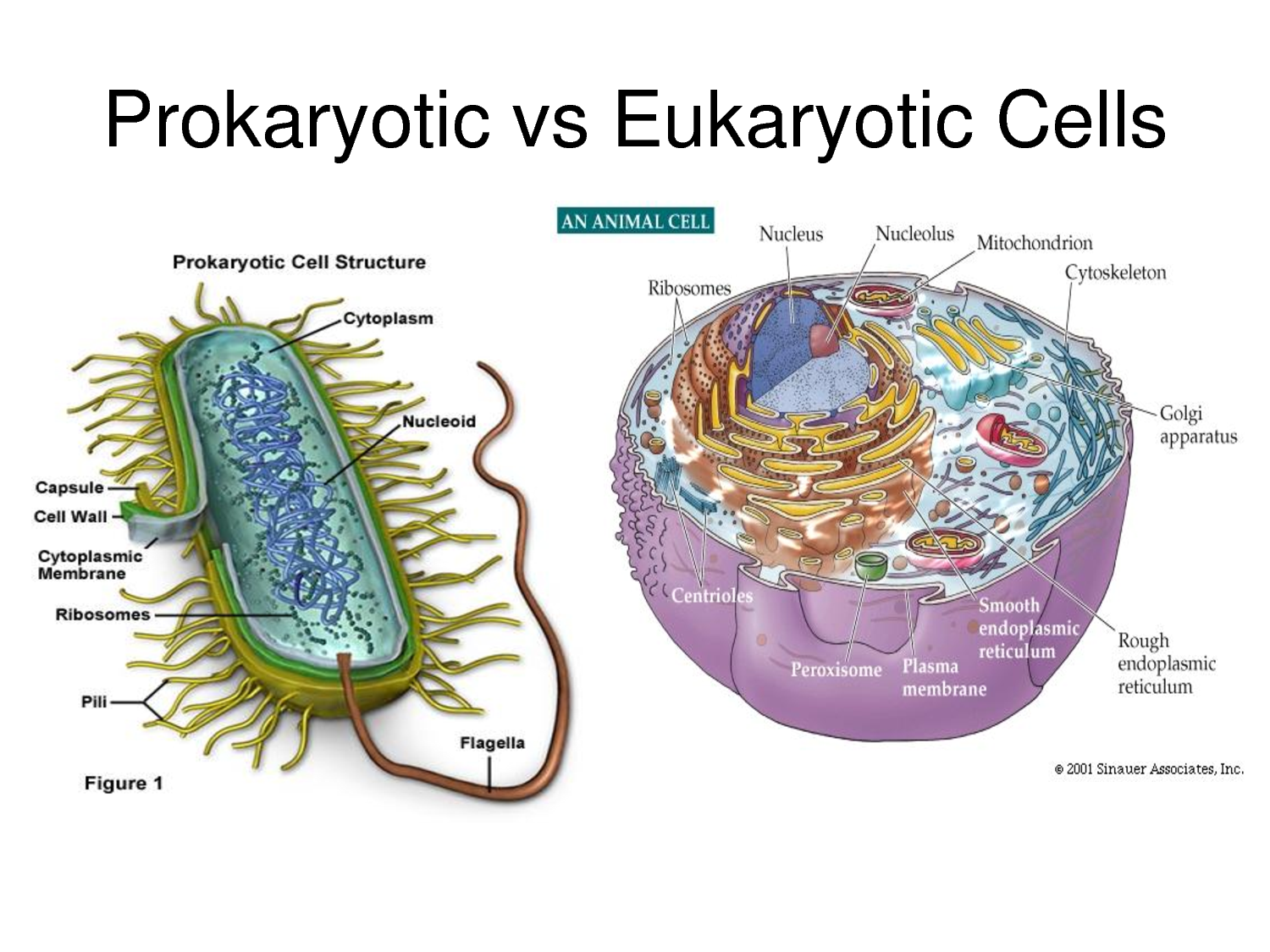
What are the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Cell Size. At 0.1-5.0 µm in diameter, prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, which have diameters ranging from 10-100 µm (Figure 3.7). The small size of prokaryotes allows ions and organic molecules that enter them to quickly spread to other parts of the cell. Similarly, any wastes produced within a prokaryotic.
venn diagram prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Masaka
Directions: Write in the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Smaller (1-5 um) No membrane bound organelles Reproduces by binary fission Undergoes Mitosis/Meiosis to make new cells • Ribosomes Ribosomes present present • Has Has cytoplasm cytoplasm • Has Has plasma plasma membrane membrane
Prokaryotic Cells Vs Eukaryotic Cells Venn Diagram General Wiring Diagram
Google Classroom Universal features of cells. Characteristics of prokaryotic cells. Surface area-to-volume ratio. Introduction Take a moment and look at yourself. How many organisms do you see? Your first thought might be that there's just one: yourself.
.PNG)
Cell Types and Cell Structure Presentation Biology
The main differences are given below. Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Venn Diagram What is the Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells What do Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have in Common Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are alike in some ways and share some common features that are given below:
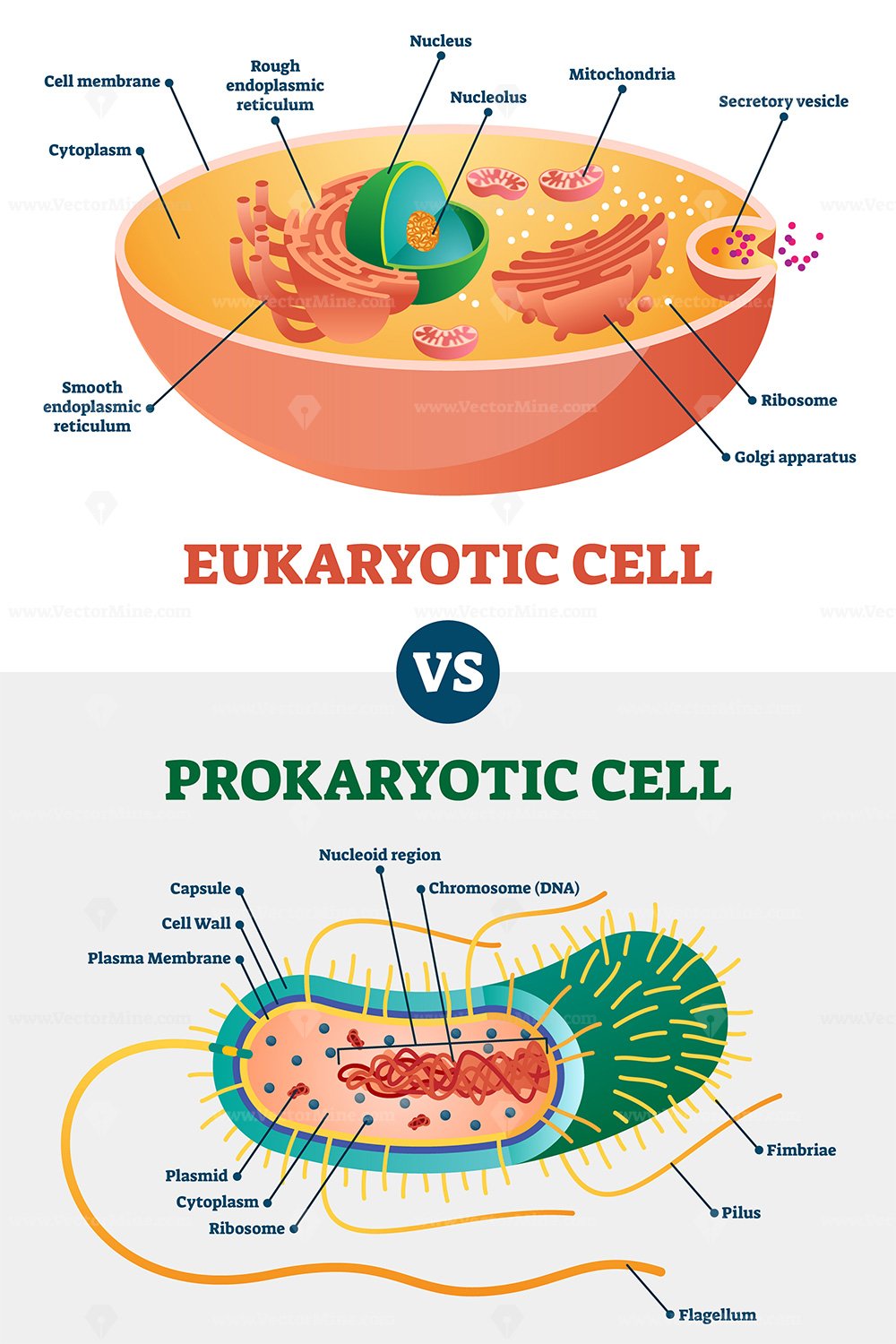
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic cells, educational biology vector
Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells are the two main types of cells that make up all living organisms on Earth. While both types of cells have similarities, they also have distinct differences. One way to compare and contrast these two types of cells is by using a Venn diagram, which illustrates the similarities and differences between the two.
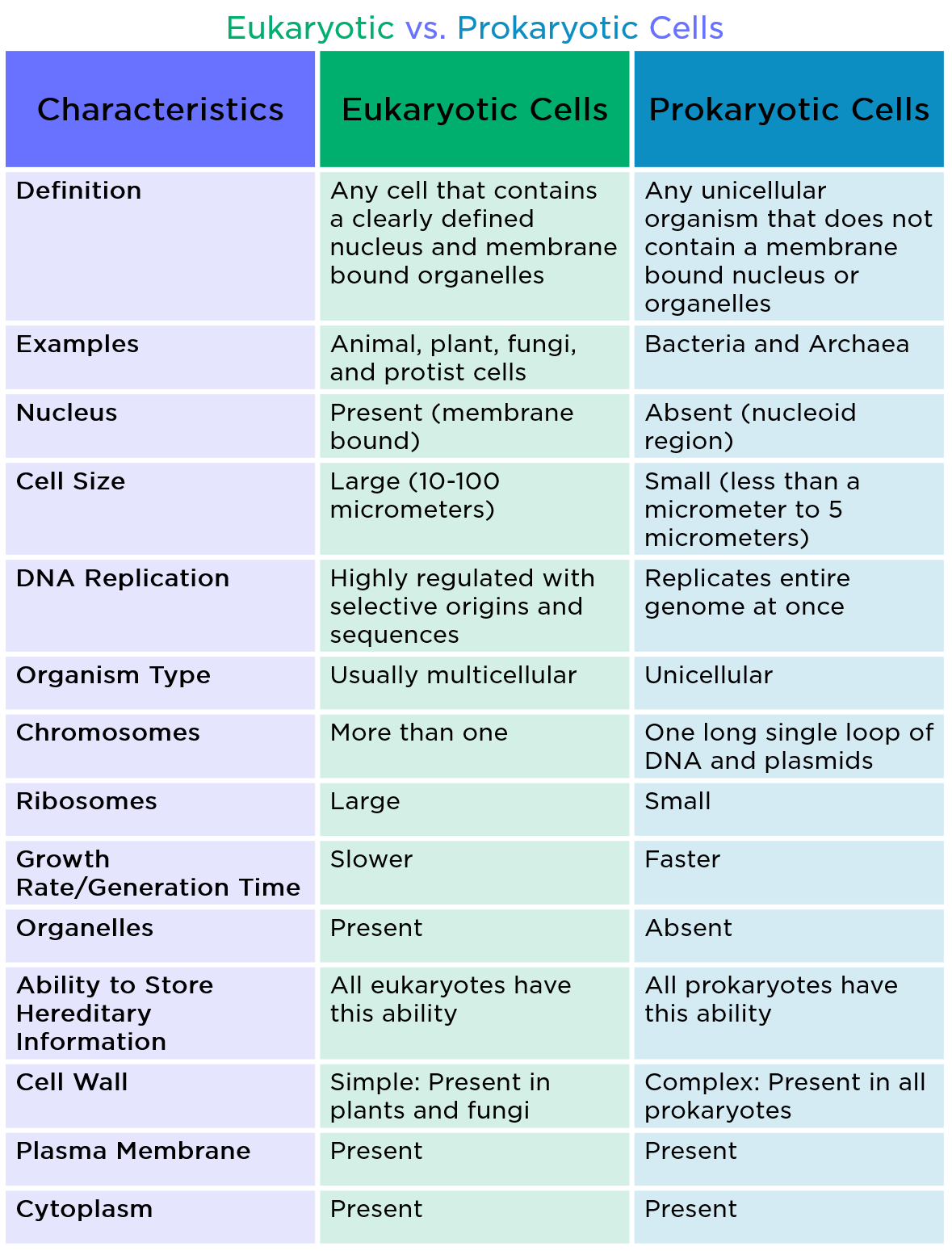
Prokaryotic Cell — Definition & Examples Expii
Eukarya The organisms in Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotes, while the organisms in Eukarya have eukaryotic cells. The Archaea domain has subcategories, but scientific sources differ on whether these categories are phyla or kingdoms. They are: Crenarchaeota Euryarchaeota Korarchaeota

Differences Between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell BYJU’S
A prokaryotic cell is a simple, single-celled (unicellular) organism that lacks a nucleus, or any other membrane-bound organelle. We will shortly come to see that this is significantly different in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic DNA is found in the central part of the cell: a darkened region called the nucleoid ( Figure 3.5 ).
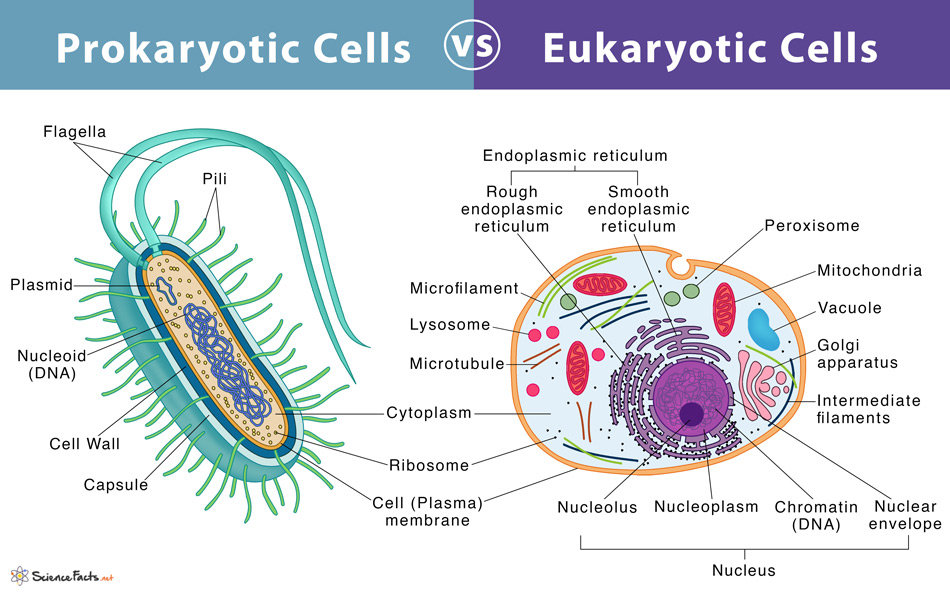
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Definition and Characteristics
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes share some similarities, but have many differences. Eukaryotes have an enclosed nucleus, while prokaryote lack membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the basic units of life on Earth.

Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Venn Diagram Plant and animal cells
A venn diagram can be used to illustrate these similarities and differences visually. Eukaryotic Cells: Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They are typically larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells have a distinct membrane-bound nucleus that houses their genetic material (DNA).

microbiology prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Google Search
Prokaryotes typically measure 0.2 - 2.0µm in diameter, whereas eukaryotic cells are 1 - 100 µm in diameter. Types of Organisms There are only two types of prokaryotic organisms on Earth, and those are bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotes are far more diverse and include animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Reproduction